Stumped by the dropping customer loyalty and employee morale? Then you are here not by chance. Let’s see how a process introduced to Motorola by Bill Smith in 1980 can give you the tools and techniques to be successful at every project you do from now on.
Companies like Tesla faced the threat of death due to its Model 3 production line, while the company was bleeding money and imminent bankruptcy leading to closure. A process like the six sigma process aims to reduce the time, defects and variability in your organization. Just like it was for Tesla it’s never too late to start this process and see phenomenal results.
There are 2 main methods to Six Sigma (6σ). Known by the 2 acronyms, DMAIC & DMADV is what you need to identify the way forward.
What does DMAIC stands for?
The most commonly used method focuses on improving an existing product or service in the company.
D – Define
In this stage, you will look at the problem as a whole and determine the issues you are facing, your opportunities for improvement, and the customer needs.
M – Measure
Here look at the current situation and how your company is performing with a detailed oriented approach, and how your issues are propagated resulting in the defective outcome and decreasing employee morale.
A – Analyze
Once you understand the issue and where it occurs, you can now determine what caused the issues by analyzing the data you have collected from the previous step.
I – Improve
Once you have identified the problem, now you can introduce the changes. If it was time that you needed to improve the project you can now introduce a change, or replace the problem with an alternative as a solution if it’s in production.
C – Control
Closely monitoring how changes are faring, you can now make regular adjustments to further improve or control future processers with minor adjustments to increase higher productivity and overall performance of the company.
What does DMADV stands for?
This is the ideal method used to create a new product/ service for the company. This is also known as DFSS which means Design For Six Sigma.
D – Define
In this stage, you understand the need of customers through customer input, industry research, and historical data to determine what you need to have to become successful by making your product cater to the audience.
M – Measure
Once you have defined the customers need, now you can use that to create a specification to define and measure the product so the data can be collected to compare to specific requirements.
A – Analyze
In this stage, you analyze the existing specification to find out whether there are better ways to achieve the same result with the areas of improvement being determined and tested. Based on the prototype you have created, you know whether the product is the solution to the defined customer need.
D – Design
Now that the analysis is complete with all requirements of the majority of the customers being met, you can proceed to design the first product. Revisions are made to the initial product going back and forth with the analysis stage to further develop the product. Finally, you bring a focus group to see how they receive the product and based on their feedback the final rounds of changes are made to the product.
V – Verify
In this stage, you verify whether the final product meets or exceeds the customer requirement then once it’s launched you continue to improve the product collecting customer feedback.
Below is an example of the most common tool used in the Six Sigma method known as the fishbone diagram to find the root causes of an effect. The six categories of the Fishbone Diagram are also known as the 6 Ms in the manufacturing world: man (People), machine, method, material, measurement and Mother Nature (Environment).
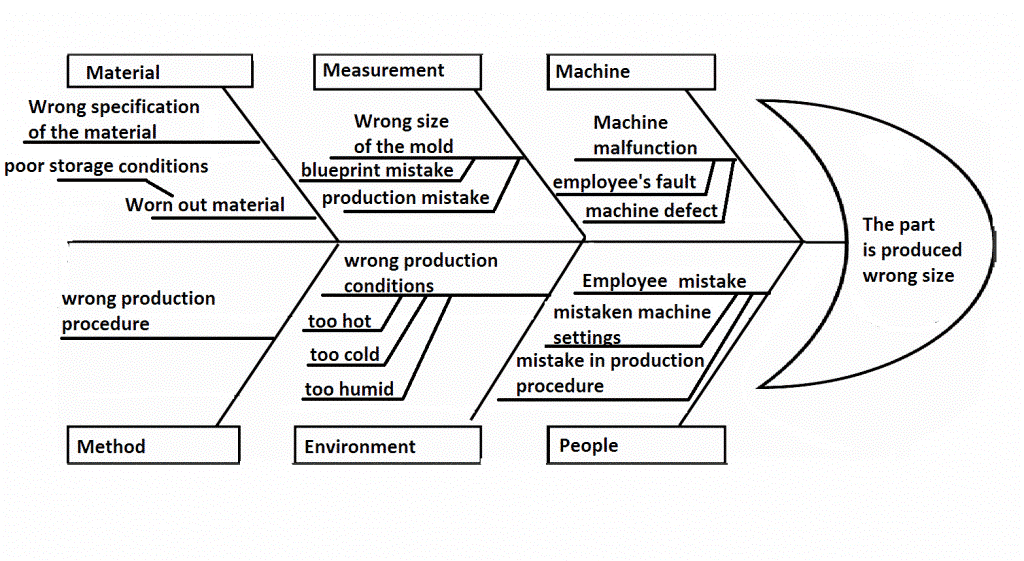
When to use this tool?
- Starting a new improvement project
- Developing a new or improved design of a process, product, or service
- Defining a repetitive work process
- Planning data collection and analysis to verify and prioritize problems or root causes
- Implementing any change
- Working toward continuous improvement
Many industries adopt the Six Sigma process to achieve their business goals. Let’s do more with less and do it even better! Share this article with your colleagues and friends. Next time if you are finding it difficult to see past a problem let’s try the Six Sigma Process.



