Marketing is not just about catchy slogans or vibrant visuals; it’s about connecting with people on a deeper level. Today, you need to promote your brand consistently through multiple channels because it takes more than 20 to 50 interactions for a person to become a paying customer.
Let’s look at how we can improve our marketing efforts with the knowledge available in neuroscience. Neuroscience is the study of the thinking behind consumer behavior, exploring how emotions drive purchasing decisions and how marketers can use this knowledge to craft more effective campaigns.
So, let’s explore how it influences our consumer choices. By the way, have you noticed the new label on the Coke bottles in Sri Lanka?
Why Emotions Trump Logic in Consumer Decisions?
The concept that we make decisions based on emotion rather than logic has been introduced previously.
However, recent advancements in neuroscience have provided more profound insights into how our brains operate when making purchasing decisions.
Rather than rational thought, emotion often takes the driver’s seat in our decision-making process.
But why is this the case?
Why Do Emotions Influence Decisions More Than Logic?
Our brains have evolved to prioritize survival, so emotional processing happens faster than rational thought.
The Amygdala, the brain’s emotional centre, reacts to stimuli much quicker than the prefrontal cortex, where logical thinking occurs.
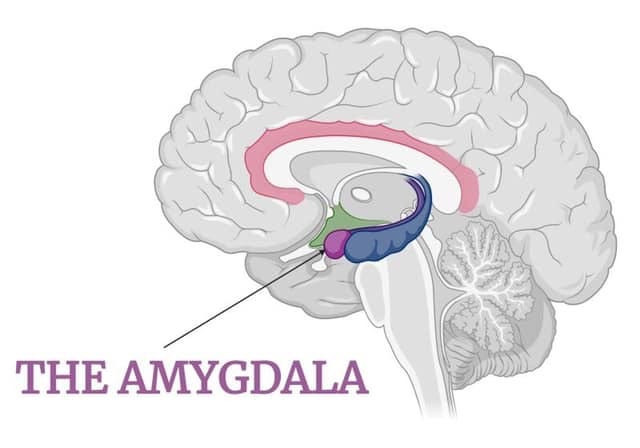
This means that when we’re faced with a decision, our emotions kick in before we’ve had the chance to think it through logically.
The Science Behind Emotional Buying
Let’s see how the brain processes emotions and affects buying decisions.
Neuroscientists have found that the brain releases dopamine, a feel-good neurotransmitter when we anticipate a reward or make a purchase.
This chemical response creates a positive association with the action, making us more likely to repeat it in the future.
Successful Emotional Marketing Campaign Examples
Airbnb’s “We Accept” Campaign – Watch the Video
Coca-Cola’s “Share a Coke” Campaign – Watch the Video
Dove’s “Real Beauty” Campaign – Watch the Video
Commercial Credit Ad – Watch the Video
How Marketers Use Emotional Triggers
Marketers have become increasingly savvy in tapping into the emotional side of consumer behaviour.
By understanding the emotional triggers that drive decisions, they can craft messages that resonate more deeply with their audience.
Here are some common emotional triggers used in marketing,
- Fear of Missing Out (FOMO): Highlighting limited-time offers or exclusive deals. Always show urgency in limiting the offer to a valid period.
- Aspiration aligns a brand with a desirable lifestyle. Many designer brands are bought by people who have risen from poverty and seek a feeling of luxury by purchasing these brands.
- Nostalgia: Creating a connection with the past to evoke positive emotions. If you’re a gamer, you might know of Call of Duty and the history behind the character Simon Ghost Riley; COD Mobile recently released a Mythic Ghost skin hyped up to the point everyone who played the old games was waiting for it because of how people were attached to the old character.
- Joy and Happiness: Associating the product with positive experiences or outcomes.
Logic: The Afterthought in Decision-Making
While emotions dominate decision-making, logic plays a crucial role but is often an afterthought.
Once the emotional decision is made, our brain uses logic to justify the choice. This is where cognitive dissonance comes into play.
If there’s a disconnect between our emotions and logic, our brain works to resolve the tension, often by finding reasons to support the emotional choice we’ve already made.
Cognitive Dissonance and Consumer Satisfaction
Cognitive dissonance occurs when beliefs or behaviors conflict.
In marketing, this can happen when a consumer makes an emotionally driven purchase but then questions whether it was the right choice.
To maintain consistency in self-perception, the brain searches for logical reasons to justify the purchase, often by focusing on the product’s positive aspects.
How Brands Build Emotional Connections
To build solid and lasting relationships with consumers, brands must go beyond selling a product. They need to sell an emotion.
This is why successful brands often have an evident brand personality that resonates with their target audience.
Whether Apple’s innovative spirit or Coca-Cola’s association with happiness, these brands have mastered creating emotional connections with consumers.
The Role of Storytelling in Emotional Marketing
One of the most effective ways to tap into consumers’ emotions is through storytelling. Stories have a unique power to engage our emotions and make us feel connected to a brand.
A well-told story can evoke empathy, excitement, or even sadness, creating a deeper bond between the consumer and the brand.
This is why many of today’s most successful marketing campaigns are built around compelling narratives.
Emotional Branding: Case Studies of Success
Let’s look at some brands that have successfully used emotional branding to their advantage:
- Nike: Through its “Just Do It” campaign, Nike taps into the emotional drive for self-improvement and determination, aligning its brand with personal empowerment.
- Dove: Dove’s “Real Beauty” campaign challenges societal beauty standards, resonating emotionally with a broad audience and fostering a sense of inclusivity and self-acceptance.
- Tesla: Tesla doesn’t just sell cars; it sells a vision of a sustainable future. By aligning its brand with environmental responsibility, Tesla connects with consumers emotionally.
The Ethical Considerations of Emotional Marketing
While leveraging emotions in marketing can be highly effective, it’s essential to approach this strategy ethically.
Manipulating consumers’ emotions to drive sales can lead to distrust and damage a brand’s reputation in the long run.
Marketers should create authentic emotional connections reflecting the brand’s values and mission.
How to Implement Emotional Marketing in Your Strategy
If you want to incorporate emotional marketing into your strategy, here are some steps to help you get started.
- Understand Your Audience: Research to understand the emotional drivers of your target audience.
- Define Your Brand’s Emotional Value: What emotions do you want your brand to evoke? Could you align your messaging accordingly?
- Use Storytelling: Craft narratives that connect with your audience emotionally.
- Leverage Emotional Triggers: Identify and incorporate emotional triggers that resonate with your audience.
- Measure the Impact: Use analytics to track the effectiveness of your emotional marketing efforts and adjust your strategy as needed.
The Future of Emotional Marketing
As technology continues to evolve, so will how we use emotional marketing. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and machine learning are already helping brands better understand and predict consumer emotions.
As these technologies become more sophisticated,
Conclusion
The human brain is a complex organ that significantly influences consumer behavior.
By understanding the neuroscience behind decision-making, marketers can develop strategies that resonate deeply with their target audience.
Tapping into emotions, rather than solely relying on logic, is paramount to building lasting brand connections.
As technology advances, so will our ability to measure and understand emotional responses.
This newfound knowledge will undoubtedly reshape the marketing landscape. However, it is crucial to use this power ethically and responsibly.
By creating authentic and meaningful experiences, brands can foster trust and loyalty while driving business growth.
Ultimately, the future of marketing lies in understanding and harnessing the emotional power of the human mind.
FAQs
How does neuroscience impact marketing strategies?
Neuroscience provides insights into how the brain processes emotions, which are the primary drivers of decision-making. Marketers can use this knowledge to create campaigns that resonate emotionally with consumers.
What is the role of cognitive dissonance in consumer behavior?
Cognitive dissonance occurs when emotions conflict with logic in decision-making. The brain resolves this by justifying the emotional choice, often focusing on the positive aspects of the purchase.
Can emotional marketing be considered manipulative?
Emotional marketing can be manipulative if not done ethically. Brands must create genuine emotional connections that reflect their actual values.
How can storytelling enhance emotional marketing?
Storytelling engages emotions and helps create a deeper connection between the consumer and the brand. A compelling narrative can evoke empathy, excitement, or other emotions that resonate with the audience.
What future trends can we expect in emotional marketing?
As AI and machine learning advance, we can expect more personalized and emotionally driven marketing experiences. These technologies will enable brands to better understand and predict consumer emotions, leading to more effective campaigns.
Further Reading
- Damasio, A. (1994). Descartes’ Error: Emotion, Reason, and the Human Brain. Harper Perennial.
- Kahneman, D. (2011). Thinking, Fast and Slow. Farrar, Straus and Giroux.
- LeDoux, J. (1996). The Emotional Brain: The Mysterious Underpinnings of Emotional Life. Simon & Schuster.
- Plassmann, H., Ramsøy, T. Z., & Milosavljevic, M. (2012). Branding the brain: A critical review and outlook. Journal of Consumer Psychology, 22(1), 18-36.
- Zaltman, G. (2003). How Customers Think: Essential Insights into the Mind of the Market. Harvard Business Review Press.









